Explore
What is the best treatment for asystole? The only two drugs recommended or acceptable by the American Heart Association (AHA) for adults in asystole are epinephrine and vasopressin. Atropine is no longer recommended for young children and infants since 2005, and for adults sinceeless electrical activity (PEA) and asystole.
What is the best treatment for asystole?
Cardiac Arrest can be any number of pulseless heart rhythm, Asystole included. Asystole however, is simply the absence of any notable electrical activity in the heart. Asystole is commonly referred to as “flatline”. due to its almost flat appearence on an Electro Cardiogram (EKG).
Is asystole the same thing as cardiac arrest?
Survival rates in a cardiac arrest patient with asystole are much lower than a patient with a rhythm amenable to defibrillation; asystole is itself not a "shockable" rhythm.
Is asystole a shockable rhythm?
The Advanced Life Support guidelines do not recommend defibrillation in asystole. They consider shocks to confer no benefit, and go further claiming that they can cause cardiac damage; something not really founder in the evidence. So why am I writing about this?
Should we shock patients in asystole?
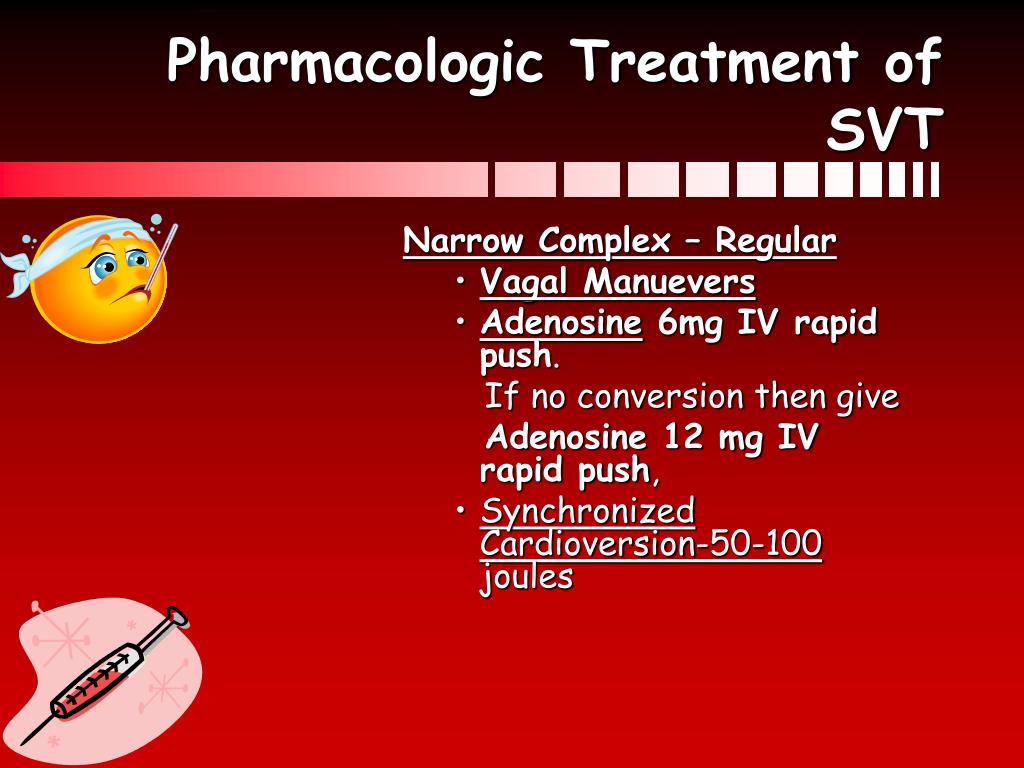
What drug do you give first for asystole?
If the rhythm check confirms asystole or PEA, resume CPR immediately. A vasopressor (epinephrine or vasopressin) may be administered at this time.
What are the initial steps of treating asystole pea?
1. Initial treatment of asystole/PEA is as follows: Continue CPR for 2 minutes....Check pulse and rhythm every 2 minutes, as follows:If nonshockable, see Nonshockable Rhythm (above).If shockable, see Shockable Rhythm (above).Rotate chest compressors.Identify and treat reversible causes.
Do you use an AED for asystole?
Children or adults who develop cardiac arrest caused by a slowing of the heart rate (bradycardia) or cardiac standstill (asystole) cannot be treated with an AED. These rhythms do not respond to electric shocks, so the AED will not allow a shock to be activated and standard CPR measures should be performed.
What is the correct treatment protocol for asystole?
Asystole is treated by cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) combined with an intravenous vasopressor such as epinephrine (a.k.a. adrenaline). Sometimes an underlying reversible cause can be detected and treated (the so-called "Hs and Ts", an example of which is hypokalaemia).
When do you give adrenaline in asystole?
When adrenaline is used, it should be used as soon as possible when the cardiac arrest rhythm is non-shockable, and after 3 defibrillation attempts for a shockable cardiac arrest rhythm.
Will an ICD shock asystole?
The wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD) can deliver shocks to terminate ventricular tachycardia and fibrillation, and also alarms for asystole and severe bradycardia events which can alert bystanders to help.
Should fine VF be treated as asystole?
If there is doubt about whether the rhythm is asystole or very fine VF, do not attempt defibrillation; instead, continue chest compressions and ventilation. Very fine VF that is difficult to distinguish from asystole is unlikely to be shocked successfully into a perfusing rhythm.
Can you shock a heart in asystole?
Asystole isn't a shockable rhythm, and defibrillation may actually make it harder to restart the heart. Defibrillation is only an option if your heart goes from asystole to a shockable rhythm, which is possible when someone with asystole receives effective CPR.
What is the best medicine for asystole?
For asystole, the standard medication to use is epinephrine.
What is an asystole?
Asystole, otherwise known as a flatline, is a state of cardiac standstill in which all electrical activity has ceased.
How often should you do a rhythm check for CPR?
Following the initial dose, epinephrine is given every 3-5 minutes as needed. During CPR, a rhythm check should be done every 2 minutes (5 cycles). These rhythm checks should be kept to less than 10 seconds, in order to prevent meaningful interruptions in CPR.
What does it mean when you have apparent asystole?
Apparent asystole may be the result of a user or technical error. If you believe the rhythm may be incorrect, ensure patches have good contact with the individual, leads are connected, the gain is set appropriately, and the power is on.
Is defibrillation effective for asystole?
Because asystole is not a shockable rhythm, defibrillation is not an effective asystole treatment. Researchers estimate that less than two percent of people who suffer asystole outside of the hospital will survive - even with trained emergency intervention.
Is asystole a flatline?
Identifying Asystole. Confirmation that the rhythm is indeed a flatline, and not a false positive, is an important part of the asystole treatment algorithm. For most patients, true asystole is the result of a prolonged illness or cardiac arrest, and prognosis is very poor.
What is Asystole?
Asystole represents the absence of both electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. Asystole is not a shockable rhythm and treatment for Asystole involves high quality CPR, airway management, IV or IO therapy, and medication therapy which is 1mg epinephrine 1:10,000 every 3-5 minutes rapid IV or IO push. It’s also important to determine the H’s and T’s to discover why the patient went into cardiac arrest and to treat any reversible causes of asystole.
How long to continue CPR?
Continue high-quality CPR for two minutes, while also attempting to establish IV or IO access.
Is asystole a shockable rhythm?
Asystole is not a shockable rhythm. So, treatment will involve high-quality CPR, airway management, IV or IO therapy, and medication therapy – specifically 1mg of epinephrine 1:10,000 concentration every 3 to 5 minutes via rapid IV or IO push.
Is asystole a shock?
Asystole is not a shockable rhythm and treatment for Asystole involves high quality CPR, airway management, IV or IO therapy, and medication therapy which is 1mg epinephrine 1:10,000 every 3-5 minutes rapid IV or IO push.
Can asystole be reversed?
It is rare for asystole to be reversed, especially after a long duration. If the patient does not respond to the BLS and ACLS treatments, the rescue team will need to decide when to stop resuscitative efforts. If there is a high degree of certainty that the patient will not respond to further ACLS interventions, it would be appropriate to stop.
When is it appropriate to stop ACLS?
If you have a high degree of certainty that the patient will not respond to further ACLS interventions , then it would be appropriate to stop.
What is the meaning of asystole on a heart monitor?
It represents the absence of both electrical and mechanical activity of the heart. Now if the patient doesn’t have a pulse and asystole is confirmed in one lead, we should check another lead and the monitor’s amplitude to make sure it is not fine V-fib. Like in PEA, it’s also important to determine the H’s and T’s to discover why the patient went into cardiac arrest and to treat any reversible causes of asystole. Remember asystole is not a shockable rhythm and treatment for asystole involves high quality CPR, airway management, IV or IO therapy, and medication therapy which is 1mg epinephrine 1:10,000 every 3-5 minutes rapid IV or IO push. It’s rare for asystole to be reversed especially after a long duration. Although it is a difficult choice to stop resuscitation efforts, if the patient does not respond to the BLS and ACLS treatments, the decision to terminate resuscitative efforts needs to be made. And if you have a high degree of certainty that the patient will not respond to further ACLS interventions, it would be appropriate to stop. The decision must be based on your specific protocols and the consideration of time from collapse to CPR, time from collapse to first defibrillation attempt, underlying causes, response to resuscitative measures, and especially the ETCO2 less than 10 after 20 minutes of CPR. All will contribute to your decision to stop resuscitative efforts in the asystole patient.
Can asystole be reversed?
Having said that, it's rare for asystole to be reversed, especially if the patient has been in asystole for a long duration of time.
Is asystole a shockable rhythm?
Pro Tip #2: Asystole is not a shockable rhythm. So, treatment will involve high-quality CPR, airway management, IV or IO therapy, and medication therapy – specifically 1mg of epinephrine 1:10,000 concentration every 3 to 5 minutes via rapid IV or IO push.
Anesthesia ACLS algorithms
These algorithms involve ACLS events in in-hospital settings for anesthetic and surgically related pathophysiology. Thank you to Vivek K. Moitra, MD, Andrea Gabrielli, MD, Gerald A. Maccioli, MD, and Michael F. O’Connor for providing this to us. Printed with permission.
Drug summary
This reference document summarizes the drugs used for ACLS cases and their storage requirements. Last updated 2015-05-07
What does ACLS stand for?
ACLS is an acronym that stands for Advanced Cardiac Life support . ACLS teaches healthcare professionals advanced interventional protocols and algorithms for the treatment of cardiopulmonary emergencies. These include primary survey, secondary survey, advanced airways, myocardial infarction, cardiac arrest, tachycardias, bradycardias, and stroke. The treatment protocols have been established through collaborative clinical research and later published by the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR).
When to follow instructions of AED?
Follow instructions of the AED until the arrival of medical transport.
How to do IO for asystole?
Pro Tip #1: Since asystole is not a shockable rhythm, you move immediately to gaining IV (or IO) access via an 18 gauge in the antecubital and call for 1mg of epinephrine 1:10,000 concentration via IV push flushed with 20cc of normal saline – to ensure the medication gets into the patient's central circulatory system. And perhaps most importantly, you instruct your team to continue CPR while the medication is being administered.
What is the purpose of an advanced airway?
At this time, you decide to secure an advanced airway to maintain the airway, give synchronous compressions with rescue breaths, and have the ability to monitor capnography.
How often should you change compressions in CPR?
You keep an eye on chest compressions and remember to change compressors every 2 minutes or if you notice fatigue setting in to ensure adequate compressions throughout the code. You tell your team that CPR is looking good or you make suggestions for improvements.
