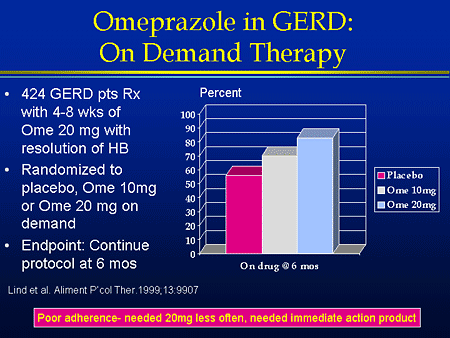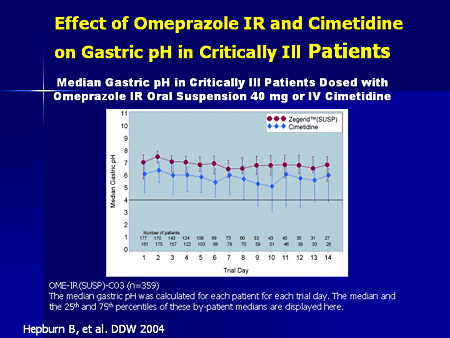
Full Answer
How long has acid treatment been used to improve well productivity?
Oil and gas operators have used acid treatment (acidizing) to improve well productivity for almost 120 years. Acidizing predates all other well stimulation techniques, including hydraulic fracturing which was not developed until the late 1940s.
How long does it take for acid to kick in?
Using these drugs can lead to criminal charges and long-term addiction. You may begin to feel the effects of one tab of acid within 20 to 90 minutes of ingesting the drug. Although the average acid trip can last anywhere from 6 to 15 hours, most trips won’t last more than 12 hours.
How long do acid trips last?
How long does it last? You may begin to feel the effects of one tab of acid within 20 to 90 minutes of ingesting the drug. Although the average acid trip can last anywhere from 6 to 15 hours, most trips won’t last more than 12 hours. After your trip is over, you may experience “afterglow” effects for another six hours.
How do I build an acid treatment evaluation?
The prime source of information on which to build an evaluation are the acid treatment report and the pressure and rate data during injection and falloff. The tasks of execution and evaluation go hand in hand. Proper execution, quality control, and record keeping are prerequisites to the task of accurate evaluation.
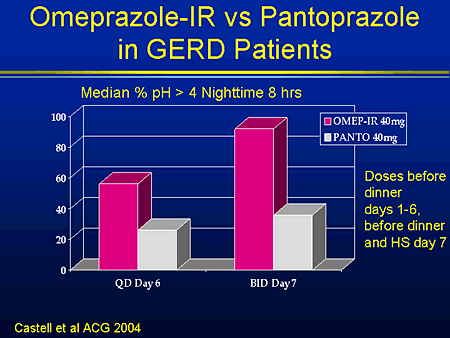
What is acid treated starch?
In this method, a concentrated starch slurry is heated in 1 to 3% HCl at about 50°C for 12–14 hours, leading to partial acid hydrolysis of the glucosidic bonds in the amorphous portion of the starch. The crystalline areas are not freely accessible to the acid and remain intact. After neutralization and recovery by filtration, the modified starch, with a lower molecular weight but with its crystalline structure intact, displays different characteristics on heating it in water. The granules fragment more and swell less, and the temperature range of gelatinization increases and, on gelatinization, the starch becomes soluble. The resulting paste is less viscous and the gels are more rigid. Acid-modified starches are used in jelly beans and other gum confectioneries.
What is acid treatment?
Acid treatment, i.e. addition of inorganic or organic acids, is used both for forage and cereal grains and results in a rapid decrease in pH , which efficiently prevents the growth of most microorganisms. Acid treatment inactivates the sprout and interferes with the baking process, and thus is not appropriate for storage of grain intended for baking or malting (Jonsson 1997 ). Acid application is a delicate process and needs to be monitored accurately as addition of the correct concentrations of acid depends on the water content of the crop ( Lacey and Magan 1991 ). Uneven distribution of acid over the kernel surface may permit mould growth during storage as inaccurate dosage of formic acid has, for example, been shown to increase the risk of aflatoxin production ( Clevstroöm et al. 1989 ). Low concentrations of propionate may also stimulate the production of aflatoxins ( Al-Hilli and Smith 1979 ).
Does LA stimulate glucose uptake?
LA treatment of ZDF rats and streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats markedly enhanced insulin-stimulated glucose uptake into the muscles, as well as reduced plasma glucose levels. 34,35 The studies concentrated on mechanisms by which LA stimulates glucose uptake revealed the engagement of LA in the insulin signaling pathway. It has been shown that this compound increased tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS-1 and activated both PI3K and the serine/threonine kinase Akt1, resulting in GLUT1 and GLUT4 translocation to the plasma membrane in L6 muscle cells and 3T3-L1 adipocytes. 36,37 However, the GLUT4 translocation is not sufficient itself to cause a maximum stimulation of glucose uptake. To achieve effective glucose transport, LA has to stimulate the intrinsic activity of GLUT4 via a p38 MAPK-dependent pathway in addition to GLUT4 translocation. 38 Taken together, stimulation of glucose uptake by LA comprises two mechanisms: the IRS-1/PI3K/Akt-dependent translocation of GLUT4 to the plasma membrane and p38 MAPK-dependent stimulation of their intrinsic activity. Recently, computer modeling studies by Diesel et al.39 identified a binding site for LA at the tyrosine kinase domain of IR, confirming, along with the above-described results, that LA is insulin mimetic.
Does acid treatment cause DNA to turn red?
Acid treatment, even if mild, brings about at least partial apurinization of DNA and thus changes its stainability by AO. As a result, AO forms dimers at depurinized regions, thus causing the DNA red fluorescence. This makes it necessary to avoid the presence of acids in fixatives used for AO conventional fluorescence microscopy of nucleic acids. At the same time it opens up important possibilities for the investigation of the DNA state in situ.
What temperature is sandstone acidized?
Gdanski and Schuchart developed a geochemical model for sandstone acidizing that is helpful to engineers dealing with acidizing of sandstone containing sensitive minerals like zeolite and chlorite clay and for formation temperatures above 200°F. Above 200°F, various organic acids are recommended for certain minerals.
What acid mixtures improve the performance of two Brazilian water injection wells?
These acid mixtures improved the performance of two Brazilian water-injection wells by removing deep clay damage. A preflush of HCl or acetic acid must be used to dissolve carbonates ahead of the fluosilicic acid to prevent tertiary precipitation of calcium/aluminum fluoride complexes.
How much acid can dissolve plugging solids?
If acid can easily reach nearby plugging solids, small volumes of 25 to 50 gal/ft of HF-type acid can dissolve this damage; however, with more severe damage, more time and volume are needed to reach the plugging solids. Effective acid diversion reduces acid volumes needed.
What is LSD in medicine?
Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), or acid as it’s commonly known, is a potent, long-lasting psychoactive drug. In part, it’s derived from a fungus that grows on rye and other grains. The synthetic drug has a chemical structure similar to serotonin, a “feel-good” chemical in your brain. When acid molecules land on serotonin receptors, ...
How much LSD is in a quarter inch tab?
However, a quarter-inch tab from a blotter paper typically contains 30 to 100 micrograms. An LSD gelatin, or “window pane,” may contain slightly more acid per piece.
What is acid in a paper?
Acid is a colorless, odorless liquid. For consumption, an acid manufacturer typically drips the liquid onto absorbent, colorful paper squares called blotter papers. Each blotter paper can have several “tabs.”. One tab is usually enough to induce a trip. LSD is also sometimes sold as capsules, pills, or sugar cubes.
How long does it take for acid to go away?
Although the average acid trip can last anywhere from 6 to 15 hours, most trips won’t last more than 12 hours. After your trip is over, you may experience “afterglow” effects for another six hours.
How long does it take for serotonin to fade?
The drug’s effects won’t begin to fade until the molecules are knocked off or come loose from the serotonin receptor. This can take anywhere from 6 to 15 hours. It all depends on the potency of the drug, your size, and any other medications you might be taking.
What is a flashback in acid trip?
It causes sensory disturbances similar to what you experience during a trip. These “flashbacks” can occur days, weeks, or even months after your last acid trip.
How long does acid stay in your urine?
Traces of acid will be detectable in your urine for five days and in your hair follicles for 90 days after ingestion. Read on to learn more about what to expect during a trip and why these effects last so long.
Abstract
Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) have a great potential in wide applications due to their extraordinary physical, thermal and mechanical properties. However, the known shortcomings, such as hydrophobic nature, poor solubility and dispersibility in most solvents have impeded the technology to further develop.
1. Introduction
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are visualized as hollow cylindrical graphitic nanomaterials with carbon atoms linked in hexagonal shapes. Generally, CNTs are classified into two types, which are single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs).
3. Results and discussion
In this experiment work, as-synthesized MWCNTs were used for further study on acid funtionalization treatment via varying the operating parameters. According to [ 40 ], as-synthesized MWCNTs has higher purity and more oxygenated functional groups attached on the surface as compared to the conventional as-synthesized MWCNTs.
4. Conclusion
The acid functionalization of MWCNTs is dependent on the process parameters such as concentration of acid (s) used, amount of MWCNTs, operating temperature, treatment methods durations.
Acknowledgement
Authors would like to thank Curtin University Malaysia for providing access to online sources of information required to complete this technical paper. Author would also like to thank Yayasan Biasiswa Sarawak Tunku Abdul Rahman (YBSTAR) for providing scholarship to carry out the experiment.
Abstract
Acidic oxidation methods have been widely reported as an effective method to purify and functionalize the surface of carbon nanotubes (CNTs).
1. Introduction
The potential of CNTs in mechanical, electrical, electronic, thermo-mechanical, optical and sensoring applications is nowadays undisputable [1], [2], [3]. One of the key factors needed to convert such a potential into a reality is the achievement of adequate CNT dispersion.
4. Conclusions
Five mild sonochemical oxidation treatments based on nitric and sulfuric acids have been investigated to functionalize the surface of MWCNTs. Relative low acid concentrations of HNO 3 or a mixture of HNO 3 and H 2 SO 4, short treatment times (2 h) and low sonication power were employed in order to minimize CNT damage.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by CONACyT (Mexico) project no. 79609 directed by Dr. Avilés. Dr. FA greatly appreciate fruitful discussion with Dr. Oliver Jost, Dr. Andreas Leson (Fraunhofer-IWS, Germany) and Dr.
Popular Answers (1)
I would recommend to follow Menna's procedure which afford selectively oxidized carbon nanotubes ( https://www.researchgate.net/publication/258000808_Selectivity_of_chemical_oxidation_attack_of_single-wall_carbon_nanotubes_in_solution ).
All Answers (11)
Concentration of H2SO4:HNO3? If it is concentrated (usually 98% sulfuric, 70% for nitric, you are destroyng your SWCNT. Not by temperature in my opinion. But if still want to use such concentrations, try to reflux lower time (3 h) and add water after (2L... more or less) and stirring overnight.
Similar questions and discussions
How to functionalize CNT using concentrated sulfuric acid and nitric acid?
What is acidizing oil?
Acidizing: Treatment in Oil and Gas Operators. Oil and gas operators have used acid treatment (acidizing) to improve well productivity for almost 120 years. Acidizing predates all other well stimulation techniques, including hydraulic fracturing which was not developed until the late 1940s. However, until the early 1930’s, acidizing use was limited ...
Why is acidizing important?
Today, acidizing is one of the most widely used and effective means available to oil and gas operators for improving productivity (stimulation) of wells. Acidizing is commonly performed on new wells to maximize their initial productivity and on aging wells to restore productivity and maximize the recovery of the energy resources.
What is Nitters et al.'s approach to candidate selection?
present a systematic approach for candidate selection, damage evaluation, and treatment selection and design using a recently developed integrated software package. They recognize the importance of evaluating skin factors from well tests to determine what could be improved. After identifying damage mechanisms, they used an expert system and geochemical simulator to select appropriate treatment fluids. They also developed software for the evaluation and design of acid placement.
What happens if the well injectivity or productivity (after the well returns to injection or production) is not close to
If the well injectivity or productivity (after the well returns to injection or production) is not close to that predicted by the falloff analysis, some damage probably occurred to the formation after the acid treatment ended.
What is the most important measure of the treatment?
The most important measure of the treatment is the productivity of the well after treatment. When the productivity stabilizes at the same production rate as before treatment, the flowing bottomhole pressure should be estimated from fluid levels or from measured flowing pressures.
What is treatment evaluation?
Treatment evaluation leads to problem identification and to continuously improved treatments. The prime source of information on which to build an evaluation are the acid treatment report and the pressure and rate data during injection and falloff. The tasks of execution and evaluation go hand in hand. Proper execution, quality control, and record keeping are prerequisites to the task of accurate evaluation. Evaluation of unsatisfactory treatments is essential to recommending changes in chemicals and/or treating techniques and procedures that will provide the best treatment for acidizing wells in the future.
Why is it important to evaluate unsatisfactory treatments?
Evaluation of unsatisfactory treatments is essential to recommending changes in chemicals and/or treating techniques and procedures that will provide the best treatment for acidizing wells in the future.
How to acidize a well?
Successful acidizing is assured by proper treatment design, well preparation, and execution, which includes significant practices: 1 Acid cleaning of tubing 2 Acid type and concentration designed for the mineralogy and the permeability of the formation 3 Acids, additives, and solvent flush designed for proper acid/reservoir fluid compatibility 4 Properly prepared wellbore and effective acid coverage 5 Sufficient time provided for acid contact and penetration of all perforations 6 Precipitation prevented or flushed away from the wellbore
When should falloff pressures be recorded?
Falloff pressures. If the pressure exists at the wellhead, the falloff pressures should be recorded on site until the well goes on vacuum. If the well goes on vacuum too soon, fluid levels can be shot with a sonolog device until the level falls to near the static bottomhole pressure.