What is the treatment of aneurysm?
The only way to get rid of an aneurysm is to have it repaired with surgery or an endovascular procedure. Sometimes surgery isn't possible, or it may pose more danger than the aneurysm. Careful monitoring and medication may be best in that case. Your doctor will figure out the size, type, and location of the aneurysm.
What are three treatments of an aneurysm?
Broadly, three treatment options for people with the diagnosis of cerebral aneurysm include:medical (non-surgical) therapy.surgical therapy or clipping and.endovascular therapy or coiling with or without adjunctive devices.
Can you treat an aneurysm without surgery?
Brain aneurysms can be treated either surgically or through an endovascular approach. About 50 percent of the aneurysms treated through an endovascular procedure, without the need for direct surgery.
What is the procedure for a brain aneurysm?
Endovascular coiling is a procedure performed to block blood flow into an aneurysm (a weakened area in the wall of an artery). Endovascular coiling is a more recent treatment for brain aneurysms; it has been used in patients since 1991.
How do you treat an aneurysm naturally?
11 Tips to Help Reduce Your Risk of an AneurysmMake Healthy Choices in Your Diet. ... Keep Your Blood Pressure Levels in Check. ... Lower High Cholesterol. ... Make Exercise a Part of Your Routine. ... Take Steps to Reduce and Manage Stress Well. ... 10 Tips to Help You De-Stress. ... Treat Obstructive Sleep Apnea. ... Quit Smoking.More items...•
What is the treatment for unruptured brain aneurysm?
Endovascular coiling A surgical clip, an endovascular coil or a flow diverter can be used to seal off an unruptured brain aneurysm and help prevent a future rupture.
Can an aneurysm be treated with medication?
If you require emergency treatment because of a ruptured brain aneurysm, you'll initially be given a medication called nimodipine to reduce the risk of the blood supply to the brain becoming severely disrupted (cerebral ischaemia). Either coiling or clipping can then be used to repair the ruptured brain aneurysm.
Can you recover from an aneurysm?
It will take 3 to 6 weeks to fully recover. If you had bleeding from your aneurysm this may take longer. You may feel tired for up to 12 or more weeks. If you had a stroke or brain injury from the bleeding, you may have permanent problems such as trouble with speech or thinking, muscle weakness, or numbness.
Can the body repair an aneurysm?
Although it is possible to repair a ruptured aneurysm surgically, it's important to identify and treat aneurysms before a rupture occurs. An aneurysm that causes internal bleeding requires open surgery aneurysm repair.
How successful is brain aneurysm surgery?
One hundred forty-three (96.62%) aneurysms were successfully clipped, and 3.37% were either wrapped or later coiled. Surgical-related mortality was 0.82% (1 patient because of air embolism).
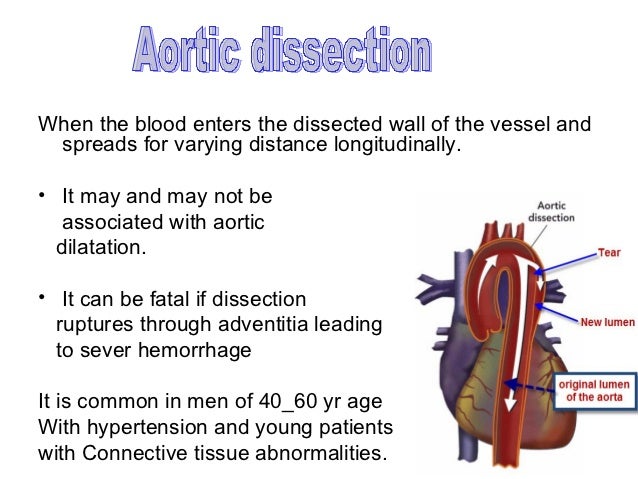
What happens with an aneurysm?
An aneurysm is a bulge in a blood vessel caused by a weakness in the blood vessel wall, usually where it branches. As blood passes through the weakened blood vessel, the blood pressure causes a small area to bulge outwards like a balloon.
What is brain aneurysm surgery called?
Endovascular coiling is another surgical procedure used for aneurysms. It's less invasive than surgical clipping. During endovascular coiling, a catheter is inserted into an artery in your groin and threaded to your aneurysm. The catheter then releases tiny coils of wire into the aneurysm, helping to block blood flow.
How to treat an aneurysm in the brain?
A surgical procedure to treat brain aneurysms involves opening the skull, finding the affected artery and then placing a metal clip over the neck of the aneurysm.
How to reduce the risk of brain aneurysm rupture?
If you have an unruptured brain aneurysm, you may lower the risk of its rupture by making these lifestyle changes: Don't smoke or use recreational drugs. If you smoke or use recreational drugs, talk to your doctor about strategies or an appropriate treatment program to help you quit. Eat a healthy diet and exercise.
What blood test is done for subarachnoid hemorrhage?
Cerebrospinal fluid test. If you've had a subarachnoid hemorrhage, there will most likely be red blood cells in the fluid surrounding your brain and spine (cerebrospinal fluid). Your doctor will order a test of the cerebrospinal fluid if you have symptoms of a ruptured aneurysm but a CT scan hasn't shown evidence of bleeding.
What tests are used to determine if you have an aneurysm?
Diagnostic tests include: Computerized tomography (CT). A CT scan, a specialized X-ray exam, is usually the first test used to determine if you have bleeding in ...
How to close off a brain aneurysm?
There are two common treatment options for a ruptured brain aneurysm. Surgical clipping is a procedure to close off an aneurysm. The neurosurgeon removes a section of your skull to access the aneurysm and locates the blood vessel that feeds the aneurysm.
What is the purpose of MRI?
An MRI uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the brain, either 2-D slices or 3-D images. A type of MRI that assesses the arteries in detail ( MRI angiography) may detect the presence of an aneurysm. Cerebral angiogram.
What is the test called for aneurysms?
This variation of the test is called CT angiography. Cerebrospinal fluid test.
What is the goal of aneurysm treatment?
The main goal of aneurysm treatment is preventing a rupture. Imaging tests can help the doctor determine if immediate surgical treatment is necessary. In some cases, careful monitoring may be the most appropriate course.
What can be done to repair an aneurysm?
If an aneurysm is likely to rupture, a variety of surgical procedures can divert blood flow away from the aneurysm and repair the affected blood vessel, including microsurgical clipping, artery bypass and occlusion, flow diversion with stents and endovascular coiling.
What is the term for a bulge in the brain?
A brain aneurysm (also called a cerebral aneurysm or an intracranial aneurysm) is a balloon-like bulge arising from a weakened area in the wall of a blood vessel in the brain.
Can an unruptured brain aneurysm be detected?
Unruptured brain aneurysms do not always produce symptoms, and sometimes they are discovered when a doctor is examining a patient for another reason. People diagnosed with an unruptured brain aneurysm should consult a medical team that specializes in brain aneurysm surgery.
Where is an aneurysm located?
An aneurysm may also be located in the blood vessels of the brain (cerebral aneurysm). Aneuyrisms can also develop in the blood vessels of the neck, the intestines, the kidney, the spleen or the legs. When caught in time, aneurysms can be treated with surgery.
What is the risk of an aneurysm?
The larger an aneurysm becomes, the greater the risk for rupture (bursting), which can result in life-threatening bleeding. Risk factors for aneurysm include older age, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, family history and high blood pressure.
Where is the most common location of an aneurysm?
The most common location of an aneurysm is the aorta, the largest artery, which carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the body. Aortic aneurysms may be thoracic – located in the segment of the aorta in the chest cavity, or abdominal – in the part of the aorta that runs through the abdomen.
What is the goal of treatment for an aortic aneurysm?
Treatment. The goal of treatment — either medical monitoring or surgery — is to prevent your aneurysm from rupturing. Which treatment you have depends on the size of the aortic aneurysm and how fast it's growing.
What is the goal of abdominal aneurysm treatment?
The goal of abdominal aortic aneurysm treatment is to prevent an aneurysm from rupturing. Treatment may involve careful monitoring or surgery. Which treatment you have depends on the size of the aortic aneurysm and how fast it's growing.
What is watchful waiting for an aneurysm?
A doctor might recommend this option, also called watchful waiting, if the abdominal aortic aneurysm is small and isn't causing symptoms. Monitoring requires regular doctor's checkups and imaging tests to determine if the aneurysm is growing and to manage other conditions, such as high blood pressure, that could worsen the aneurysm.
What test can be used to diagnose an aortic aneurysm?
If your doctor suspects that you have an aortic aneurysm, specialized tests, such as the following, can confirm it. Abdominal ultrasound. This test is most commonly used to diagnose abdominal aortic aneurysms. You lie on a table while a technician moves a wand (transducer) around your abdomen.
How to repair an aneurysm in the aorta?
Depending on several factors, including location and size of the aneurysm, your age, and other conditions you have, repair options might include: Open abdominal surgery. This involves removing the damaged section of the aorta and replacing it with a synthetic tube (graft), which is sewn into place.
When is an aortic aneurysm found?
Abdominal aortic aneurysms are often found when a physical exam is done for another reason or during routine medical tests, such as an ultrasound of the heart or abdomen.
How big is an aneurysm?
Repair is generally recommended if your aneurysm is 1.9 to 2.2 inches (4 .8 to 5.6 centimeters) or larger or if it's growing quickly. Also, your doctor might recommend surgery if you have symptoms such as stomach pain or you have a leaking, tender or painful aneurysm.
What is cerebral aneurysm?
A cerebral or intracranial aneurysm is an abnormal focal dilation of an artery in the brain that results from a weakening of the inner muscular layer (the intima) of a blood vessel wall. The vessel develops a "blister-like" dilation that can become thin and rupture without warning. The resultant bleeding into the space around ...
How big is an aneurysm?
Aneurysms range in size, from small – about 1/8 inch – to nearly one inch. Aneurysms larger than one inch are called giant aneurysms, pose a particularly high risk and are difficult to treat. The exact mechanisms by which cerebral aneurysms develop, grow and rupture are unknown.
What is the risk of rupture of an aneurysm in the anterior circulation?
The study suggested that aneurysms < 7 mm in the anterior circulation have 0.05 percent risk of rupture and should be observed. This study could not make recommendations regarding the modality of treatment because the characteristics of patients in the endovascular cohort differed greatly from those in the surgical group (3).
How is an aneurysm clipped?
An aneurysm is clipped through a craniotomy, which is a surgical procedure in which the brain and the blood vessels are accessed through an opening in the skull. After the aneurysm is identified, it is carefully dissected (separated) from the surrounding brain tissue. A small metal clip (usually made from titanium) is then applied to the neck (base) of the aneurysm. Aneurysm clips come in all different shapes and sizes, and the choice of a particular clip is based on the size and location of an aneurysm. The clip has a spring mechanism which allows the two "jaws" of the clip to close around either side of the aneurysm, thus occluding (separating) the aneurysm from the parent (origin) blood vessel. In the ideal clipping, normal blood vessel anatomy is physically restored by excluding the aneurysm sac from the cerebral circulation.
What is an unruptured aneurysm?
An un-ruptured aneurysm is the one whose sac has not previously leaked. Every year approximately 30,000 patients in the U.S. suffer from a ruptured cerebral aneurysm, and up to 6 percent of the population may have an un-ruptured cerebral aneurysm.
When was endovascular treatment first used?
Endovascular techniques for treating aneurysms date back to the 1970s with the introduction of proximal balloon occlusion by Fjodor A. Serbinenko, MD, a Russian neurosurgeon. During the 1980s, endovascular treatment of aneurysms with balloon occlusions was associated with high procedural rate of rupture and complications. Guido Guglielmi, MD, an American-based neuroradiologist, invented the platinum detachable microcoil, which was used to treat the first human being in 1991. The development of Guglielmi detachable coils (GDCs), and their FDA approval in 1995, revolutionized endovascular treatment of cerebral aneurysms.
Where is the balloon placed for aneurysm coiling?
For balloon-assisted coiling, the balloon is temporarily inflated at the neck of the aneurysm while the coils are placed into the aneurysm. For stent-assisted coiling, the stent is permanently placed across the aneurysm neck. There are advantages and disadvantages of both approaches.
What happens when an aneurysm grows in size?
As an aneurysm grows in size, the wall of the aorta becomes weaker and weaker, which means surgical intervention may be needed. The goal of any treatment strategy is to preventing the rupture of an aneurysm by controlling the growth of the aneurysm.
How big is an aortic aneurysm?
Guidelines for surgical intervention include: Aneurysm size > 5 cm (about 2 inches)
What is specific treatment?
Specific treatment is based on: Your age, overall health, and medical history. Extent of the disease. Your signs and symptoms. Your tolerance of specific medications, procedures, or therapies. Expectations for the course of the disease. Your opinion or preference.
How does an aneurysm test work?
It uses a dye injected into your blood vessels to make them easier to see. This test uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create images of the body part being examined. Once an aneurysm is discovered, the decision to treat it usually depends on its size or rate of growth.
Why do some people have an aortic aneurysm?
Different factors may increase your risk, including: Heart disease: The most common cause of aortic aneurysms is atherosclerosis, also known as hardening of the arteries.
What is the section of the aorta that is closest to the heart called?
The upward part of the arch, which is the section closest to the heart, is called the ascending aorta. The part of the aorta in the chest is called the thoracic aorta. The portion further down in your trunk is called the abdominal aorta. An aneurysm is a bulge that forms in the wall of an artery. It happens when the artery wall weakens.
Why is an ascending aortic aneurysm dangerous?
It happens when the artery wall weakens. Aneurysms anywhere in the body are dangerous because they can rupture and cause massive internal bleeding. An ascending aortic aneurysm is especially serious. A rupture in this part of the body can be life-threatening. Share on Pinterest.
How do you know if you have an ascending aortic aneurysm?
Some ascending aortic aneurysms never rupture or cause any noticeable symptoms. They’re often discovered by accident, when a chest X-ray or other screening reveal s a bulge in the aorta. If symptoms are present, they may include: dull pain or tenderness in the chest. cough or hoarseness.
What can weaken the aortic wall?
Infection: Sometimes, certain infections can also weaken artery walls, including those in the aortic arch. These infections include syphilis and salmonella.
What is the procedure called when a surgeon opens up the chest and replaces the damaged portion of the aor?
In this procedure, a surgeon opens up your chest and replaces the damaged portion of your aorta with a synthetic tube called a graft. In some cases, they also replace the aortic valve with a synthetic valve.
What to do if your doctor catches an aneurysm?
If your doctor catches your aneurysm before it becomes an emergency, there are some important steps to take: Tell your doctor about any medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and nutritional supplements. Quit smoking if you smoke. Don’t eat or drink anything eight hours before the procedure.
How to repair an aneurysm in the brain?
Brain aneurysm repair is done on an emergency basis so there’s often little time to prepare for it. If your doctor catches your aneurysm before it becomes an emergency, there are some important steps to take: 1 Tell your doctor about any medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and nutritional supplements. 2 Quit smoking if you smoke. 3 Don’t eat or drink anything eight hours before the procedure. 4 Take any medications your doctor gives you. 5 Stop taking any medications your doctor instructs you not to take. 6 Follow all other instructions from your doctor.
How does endovascular repair work?
Endovascular repair. During an endovascular repair, your surgeon will insert a small wire into an artery in your groin. Your surgeon will guide a small wire through that incision and through the artery that leads to the aneurysm in your brain. A catheter, which is a thin tube, follows the wire.
Why do aneurysms remain undetected?
Many aneurysms remain undetected because someone may not experience any symptoms until they rupture. A brain aneurysm could lead to stroke or brain damage if it’s not treated. If your doctor finds an aneurysm that hasn’t ruptured, they will likely recommend repairing it as quickly as possible.
How small is an aneurysm?
Generally, smaller aneurysms and aneurysms found in the arteries toward the front side of the brain are less likely to rupture. Those smaller than 7 millimeters are considered less likely to rupture. Your doctor will still likely recommend close follow-up to make sure the aneurysm is not getting larger.
What happens if a blood vessel in the brain ruptures?
If a blood vessel in your brain ruptures, it can cause bleeding in the brain or stroke. This could lead to brain damage or even death.
Is an aneurysm permanent?
They can vary in severity and they’re not always permanent.

Diagnosis
Treatment
- Surgery
There are two common treatment options for a ruptured brain aneurysm. 1. Surgical clipping is a procedure to close off an aneurysm.The neurosurgeon removes a section of your skull to access the aneurysm and locates the blood vessel that feeds the aneurysm. Then the neurosurgeon pla… - Flow diverters
Newer treatments available for brain aneurysm include tubular stent-like implants (flow diverters) that work by diverting blood flow away from an aneurysm sac. The diversion stops blood movement within the aneurysm and stimulates the body to heal the site, encouraging reconstruc…
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Coping and Support
- The Brain Aneurysm Foundation offers information on connecting with support groups in many states and in other countries, including the Mayo Clinic Brain Aneurysm Support Group.
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Brain aneurysms are often detected after they've ruptured and become medical emergencies. However, a brain aneurysm may be detected when you've undergone head-imaging tests for another condition. If such test results indicate you have a brain aneurysm, you'll need to discuss the results with a specialist in brain and nervous system disorders (neurologist, neurosurgeon o…