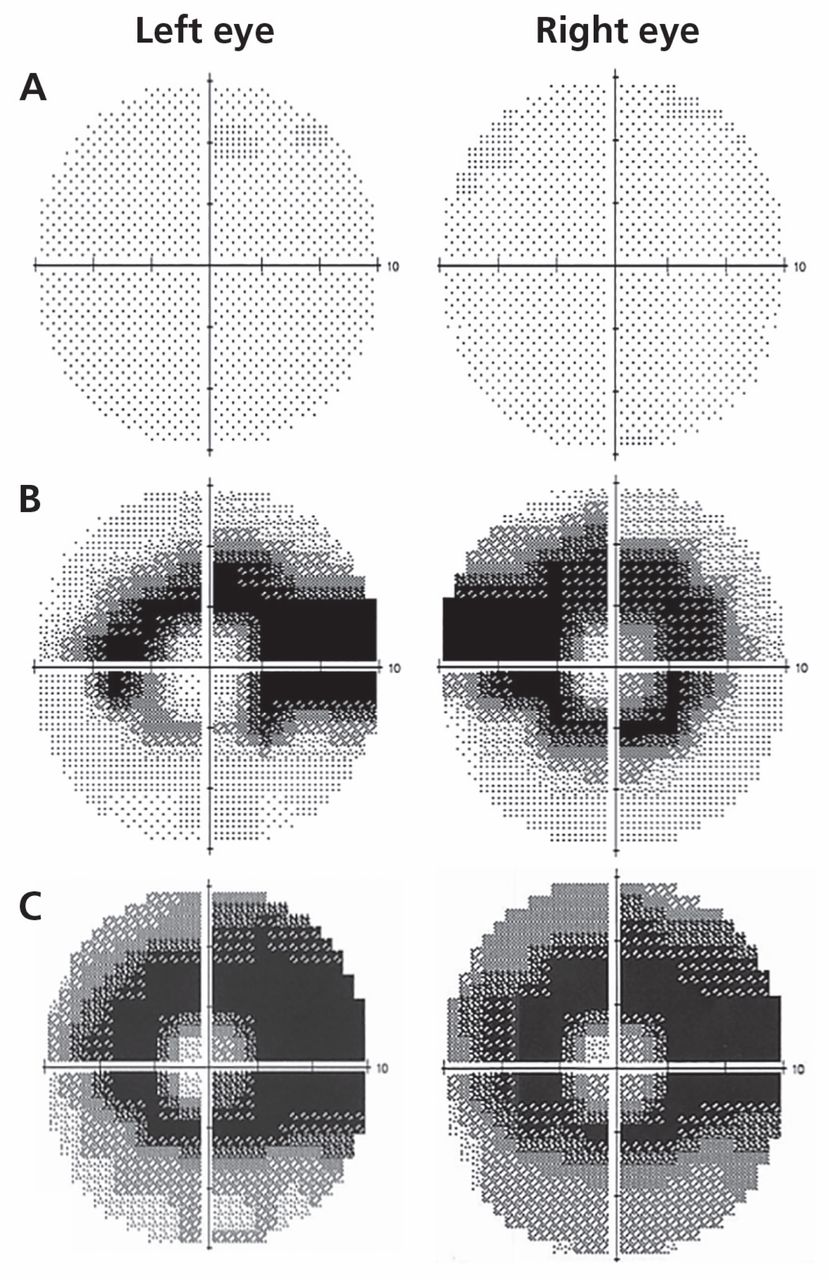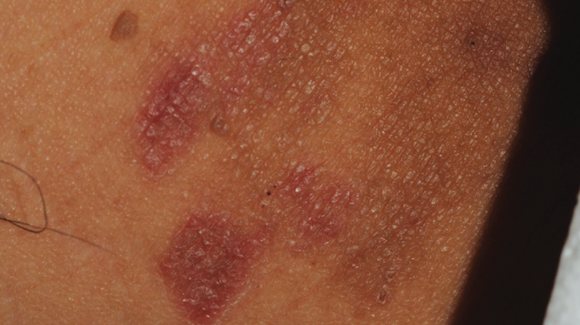
Can older adults over 65 manage their diabetes better?
Diabetic treatment goals for older adults over 65 are different from those for younger adults and children. To avoid hypoglycemia, patients with multiple chronic conditions, or who have a terminal diagnosis, can manage their blood sugar less strictly. 5 Older adults in more stable health can manage their diabetes with tighter control.
Where can I find the DVLA guidelines for cardiovascular rehabilitation?
Https://Www.gov.uk/current-medical-guidelines-dvla-guidance-for-professionals-cardiovascular-chapter-appendix. [Google Scholar] 19. British Heart Foundation. Http://Www.bhf.org.uk/heart-health/living-with-heart-disease/cardiac-rehabilitation.aspx. [Google Scholar] 20. Kwan G, Balady GJ.
Is the blood sugar target strict for the elderly?
However, the blood sugar target for the elderly is less strict compared to the ideal range for other age groups. The diabetes management plan for older adults may also be different. Hypoglycemia happens when your blood sugar levels are lower than normal.
Can type 2 diabetes be cured after age 50?
Type 2 diabetes doesn’t have a cure, but you can manage it with medications and healthy lifestyle choices as you age. Here are a few steps to take to enjoy a healthy life with type 2 diabetes after age 50: Take your medications as directed by your doctor.

How is ST elevation treated?
Which treatment you receive will depend on the results of your tests, and will be discussed between you and your heart doctor or cardiologist.Option 1: Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) ... Option 2: Thrombolysis. ... Option 3: Medications. ... Option 4: Coronary bypass surgery.
What does an elevated ST segment indicate?
ST-segment elevation usually indicates a total blockage of the involved coronary artery and that the heart muscle is currently dying. Non-STEMI heart attacks usually involve an artery with partial blockage, which usually does not cause as much heart muscle damage.
How much ST elevation is significant?
An ST elevation is considered significant if the vertical distance inside the ECG trace and the baseline at a point 0.04 seconds after the J-point is at least 0.1 mV (usually representing 1 mm or 1 small square) in a limb lead or 0.2 mV (2 mm or 2 small squares) in a precordial lead.
What are 4 signs of myocardial infarction?
What are the symptoms of acute myocardial infarction?pressure or tightness in the chest.pain in the chest, back, jaw, and other areas of the upper body that lasts more than a few minutes or that goes away and comes back.shortness of breath.sweating.nausea.vomiting.anxiety.feeling like you're going to faint.More items...
Is ST segment elevation life threatening?
ST-segment elevation is an abnormality detected on the 12-lead ECG. It is a profoundly life-threatening medical emergency and usually associated with a disease process called atherosclerosis (coronary artery disease).
Does ST elevation go away?
S-T segment elevation was present on admission in 18 of 23 patients (78 per cent) with acute anterior myocardial infarction and persisted in 13 after 1 week and in 9 of 14 (64 percent) during a follow-up period of 1 to 6 months.
How much ST elevation is considered a STEMI?
Classically, STEMI is diagnosed if there is >1-2mm of ST elevation in two contiguous leads on the ECG or new LBBB with a clinical picture consistent with ischemic chest pain. Classically the ST elevations are described as “tombstone” and concave or “upwards” in appearance.
What causes ST elevation in all leads?
The most important cause of ST segment elevation is acute Ischemia. Other causes are [4][6]: Early repolarization. Acute pericarditis: ST elevation in all leads except aVR.
Are V2 and V3 contiguous leads?
For example, leads V3 and V4 are contiguous; V1 and V2 are also contiguous; aVL and I are also contiguous; V3 and V5 are not contiguous, because lead V4 is placed between these leads. J point elevation of ≥1 mm is considered significant in all leads except leads V2 and V3.
What is the drug of choice for myocardial infarction?
The pain of myocardial infarction is usually severe and requires potent opiate analgesia. Intravenous diamorphine 2.5–5 mg (repeated as necessary) is the drug of choice and is not only a powerful analgesic but also has a useful anxiolytic effect.
What is the best treatment for myocardial infarction?
The treatment of MI includes, aspirin tablets, and to dissolve arterial blockage injection of thrombolytic or clot dissolving drugs such as tissue plasminogen activator, streptokinase or urokinase in blood within 3 h of the onset of a heart attack.
How is MI diagnosed?
An MI is diagnosed when two of the following criteria are met:Symptoms of ischemia.New ST-segment changes or a left bundle branch block (LBBB)Presence of pathological Q waves on the ECG.Imaging study showing new regional wall motion abnormality.Presence of an intracoronary thrombus at autopsy or angiography.
What age group is most likely to have diabetes?
Older adults have a higher risk of developing diabetes, with type 2 diabetes being the most common among this age group. At 21.4%, older adults aged 65 and older have the largest share of diabetes diagnoses of all age groups. 1. The American Diabetes Association recommends that adults over 45 start getting screened for diabetes ...
Why do elderly people have hypoglycemia?
This could be due to the fact that the elderly are more likely to have other chronic conditions, malnutrition, or take multiple medications. 3. Hypoglycemia can also result from taking too much of the medication used to lower blood sugar. 4 Overtreatment of diabetes in older adults is common.
What are the best medications for hypoglycemia?
The most common therapies include: 1 DPP4 inhibitors (sitagliptin, saxagliptin, linagliptin, alogliptin): One pill daily will help lower the risk of hypoglycemia. Watch out for heart failure (saxagliptin and alogliptin) and dose modification with poor renal function. 2 SGLT2 inhibitors (dapagliflozin, canagliflozin, empagliflozin): One pill daily will lower the risk of hypoglycemia. Empagliflozin is a good option for people with heart disease, and can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular death in those with type 2 diabetes. However, this medication may come with significant side effects, including renal impairment, decreased bone density, and low blood pressure. 3 GLP1 agonists (exenatide, exenatide ER, liraglutide, albiglutide, lixisenatide, dulaglutide, semaglutide): Doses are administered by daily or weekly injections. Exenatide ER and albiglutide preparation can be time-consuming. Possible side effects include nausea, diarrhea, weight loss, and pancreatitis. Sometimes gastrointestinal side effects like decrease in appetite can be sensitive for the elderly and cause significant weight loss.
What is the best way to manage diabetes?
Nutritional Therapy. Medication is just one tool for diabetes management. Diet is another way people with diabetes can manage their condition because eating, or not eating, is what impacts blood sugar.
What is the name of the needle used to check blood sugar?
Monitoring blood sugar regularly is an important part of any diabetes management plan. 6 Blood sugar checks are done with a small needle called a lancet, which is used to prick the tip of your finger. A drop of blood is placed on a test strip and a glucometer will show your blood sugar level.
Do older adults need diabetes medication?
Older adults still need medication to help control blood sugar. They’re usually taking multiple medicines for other chronic conditions, so healthcare providers must be cautious in choosing a safe and effective diabetes medication with the lowest risk for hypoglycemia and drug interactions .
Is it normal to have diabetes as you get older?
A Word From Verywell. It’s completely normal for diabetes management and treatment to change as a person gets older. Whether someone is newly diagnosed or has had diabetes for decades, there are many options to keep blood sugar levels within normal range and maintain a good quality of life.
How to manage diabetes type 2?
Many people with type 2 diabetes can manage their blood glucose levels with diet and exercise alone. Others may need diabetes pills or insulin injections, along with medicines to manage other conditions like high blood pressure and high cholesterol.
How to improve glucose levels in older people?
Be active. Walking and other forms of daily exercise can help improve glucose levels in older people with diabetes. Set a goal to be more active most days of the week, and create a plan for being physically active that fits into your life and that you can follow. Your health care team can help. Take your medicines.
How to check glucose levels?
Your diabetes management plan will cover how to: 1 Track your glucose levels. Very high glucose levels (called hyperglycemia) or very low glucose levels (called hypoglycemia) can be risky to your health. Your plan will show how often you should check your glucose and how often to get the A1C test. If you are managing your diabetes without taking insulin, you may not need to check your glucose as often. 2 Make healthy food choices. The food you eat affects glucose levels, so it’s important to learn what’s best for you to eat, how much, and when. If you are overweight, work with your health care team to come up with a plan to lose weight. 3 Be active. Walking and other forms of daily exercise can help improve glucose levels in older people with diabetes. Set a goal to be more active most days of the week, and create a plan for being physically active that fits into your life and that you can follow. Your health care team can help. 4 Take your medicines. You should take medicine as prescribed even when you feel good. Tell your doctor if you have any side effects or cannot afford your medicines. Also, let your doctor know if you have trouble taking your medicine or keeping track of your medication schedule.
What is a diabetes management plan?
Your plan will be based on your lifestyle, preferences, health goals, and other health conditions you have. As part of your plan, your doctor may prescribe one or more medications.
Why do people with type 2 diabetes not know they have it?
Some people with type 2 diabetes may not realize they have it because symptoms often develop slowly and go unnoticed. Sometimes older adults dismiss these symptoms as “getting old,” but they can be signs of a serious problem. Talk with your doctor if you have any of these symptoms. YouTube. National Institute On Aging.
How to get rid of diabetes?
Work with your doctor to set up a plan to help you make healthier food choices and get regular exercise. Get help with quitting smoking (if you smoke), because smokers are more likely than nonsmokers to develop type 2 diabetes. Make sure to ask how often you should have your glucose levels checked.
Why is it important to manage diabetes?
It’s important to manage diabetes because, over time, it can cause serious health problems like heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, eye problems, and nerve damage that may lead to amputation. Also, people with type 2 diabetes may be at greater risk for cancer and Alzheimer’s disease.
How old do you have to be to get tested for diabetes?
The risk for type 2 diabetes usually goes up with age. People who don’t have other risk factors for the condition should start getting tested after age 45. Unlike people with type 1 diabetes, people with type 2 diabetes make insulin.
What test is used to diagnose type 2 diabetes?
Tests used to diagnose type 2 diabetes include a fasting plasma glucose test and a casual plasma glucose test. Complications of Type 2 Diabetes. If your type 2 diabetes isn't controlled well, you could get serious or life-threatening complications, including: Retinopathy.
What is the most common type of diabetes in men?
Men and Type 2 Diabetes. Medically Reviewed by Michael Dansinger, MD on August 11, 2019. Type 2 diabetes, once called non-insulin dependent diabetes or adult-onset diabetes, is the most common form of diabetes, affecting 90% to 95% of the 13 million men with diabetes. The rates of diabetes have dramatically risen in all states.
What are the problems with diabetes?
Have metabolic syndrome (a cluster of problems that include high cholesterol, high triglycerides, low HDL or “good” cholesterol and high LDL or “bad” cholesterol, and high blood pressure) Don’t get up and around a lot. Eat a diet high in sugar and refined carbohydrates and low in fiber and whole grains.
Can you get Type 2 diabetes in a hospital?
Fatigue (weak, tired feeling) Blurred vision. Numbness or tingling of the hands or feet. Frequent infections of the skin or urinary tract. Rarely, a person may be diagnosed with type 2 diabetes after showing signs of it in a hospital while in a diabetic coma.
Does alcohol help with diabetes?
Studies suggest that alcohol may actually protect against diabetes. Combining data from 15 studies, researchers found that moderate alcohol consumption reduced the risk of type 2 diabetes by almost 30%. But excessive drinking increased the risk. Here, as always, the word is moderation.
Can you take insulin with diabetes?
Still, many people with diabetes need to take oral medications that lower blood sugar levels. When these aren't enough to do the job, insulin (which is inhaled and/or injected) may be necessary, sometimes along with oral drugs.