Medications to treat severe preeclampsia usually include: Antihypertensive drugs to lower blood pressure Anticonvulsant medication, such as magnesium sulfate, to prevent seizures
Full Answer
What is the treatment for preeclampsia?
The most effective treatment for preeclampsia is delivery. You're at increased risk of seizures, placental abruption, stroke and possibly severe bleeding until your blood pressure decreases. Of course, if it's too early in your pregnancy, delivery may not be the best thing for your baby.
What are the treatment guidelines for gestational hypertension?
The treatment of gestational hypertension follows a different set of guidelines than the treatment of general high blood pressure outside of pregnancy. The main goal of treatment in pregnant women is to prevent the development of more serious conditions like fetal growth restriction or placental abruption.
What is the best treatment for high blood pressure during pregnancy?
The Most Common Treatment for Pregnancy-Induced Hypertension. The most commonly used treatment options for pregnant women with high blood pressure are: Bed rest. Short-term (acute) drug therapy. Long-term (chronic) drug therapy.
Is preeclampsia considered a medical emergency?
Eclampsia—the onset of seizures in a woman with preeclampsia—is considered a medical emergency. Immediate treatment, usually in a hospital, is needed to stop the mother's seizures, treat blood pressure levels that are too high, and deliver the fetus.

What is the treatment for gestational hypertension?
If you have mild hypertension and your baby is not fully developed, your doctor will probably recommend the following: Rest, lying on your left side to take the weight of the baby off your major blood vessels. Increase prenatal checkups. Consume less salt.
What is the best treatment for pre eclampsia and eclampsia?
Medications to treat severe preeclampsia usually include:Antihypertensive drugs to lower blood pressure.Anticonvulsant medication, such as magnesium sulfate, to prevent seizures.Corticosteroids to promote development of your baby's lungs before delivery.
What is the drug treatment of choice for preeclampsia?
For emergency treatment in preeclampsia, IV hydralazine, labetalol and oral nifedipine can be used [1]. The ACOG Practice Bulletins also recommend that methyldopa and labetalol are appropriate first-line agents and beta-blockers and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors are not recommended [21, 17].
What is the first line treatment for preeclampsia?
2. Hydralazine and labetalol are the two “first line” agents used for hypertension in preeclampsia. Hydralazine is an arteriolar dilator that reduces blood pressure but may cause tachycardia.
What is the nursing management for a patient with preeclampsia?
The overall management of preeclampsia includes supportive treatment with antihypertensives and anti-epileptics until definitive treatment - delivery. In preeclampsia without severe features, patients are often induced after 37 weeks gestation after with or without corticosteroids to accelerate lung maturity.
How do you deal with preeclampsia?
What is the treatment?Rest, lying on your left side to take the weight of the baby off your major blood vessels.Increase prenatal checkups.Consume less salt.Drink at least 8 glasses of water a day.Change your diet to include more protein.
Which drug is given during hypertension?
The first are called dihydropyridine CCBs and include amlodipine (Norvasc), felodipine (Plendil), nifedipine (Procardia), and nicardipine (Cardene). The second, termed nondihydropyridine CCBs include two drugs, diltiazem (Dilacor, Cardizem, Cartia, and Tiazac), and verapamil (Calan, Covera, Isoptin, Verelan).
What is the drug of choice for hypertension in pregnancy?
Methyldopa is a drug of first choice for control of mild to moderate hypertension in pregnancy and is the most widely prescribed antihypertensive for this indication in several countries, including the US and the UK.
Antiplatelet drugs
DEVELOPMENT OF PRE-ECLAMPSIA Compared with placebo/no antiplatelet drugs: Antiplatelet drugs (mainly low-dose aspirin) are more effective at reducing pre-eclampsia in women at risk of pre-eclampsia ( high-quality evidence ).
Calcium supplementation
DEVELOPMENT OF PRE-ECLAMPSIA Compared with placebo: Calcium supplements are more effective at reducing the risk of pre-eclampsia, especially in women with low dietary calcium ( high-quality evidence ). PRETERM BIRTH Compared with placebo: Calcium supplementation seems no more effective at reducing preterm birth ( moderate-quality evidence ).
Antioxidants
DEVELOPMENT OF PRE-ECLAMPSIA Compared with placebo/no antioxidant: We don't know whether antioxidants are more effective at reducing the risk of pre-eclampsia ( low-quality evidence ). PRETERM BIRTH Compared with placebo/no antioxidant: Vitamin C plus E seems no more effective at reducing preterm births ( moderate-quality evidence ).
Marine oil (fish oil) and other prostaglandin precursors (evening primrose oil)
DEVELOPMENT OF PRE-ECLAMPSIA Compared with placebo or no treatment: Marine oil seems no more effective at reducing the risk of pre-eclampsia ( moderate-quality evidence ). PRETERM BIRTH Compared with placebo or no treatment: Marine oil seems no more effective at reducing preterm birth (moderate-quality evidence).
Glyceryl trinitrate
DEVELOPMENT OF PRE-ECLAMPSIA Compared with placebo/no treatment: Glyceryl trinitrate may be no more effective at reducing the risk of pre-eclampsia ( low-quality evidence ).
Magnesium supplementation
DEVELOPMENT OF PRE-ECLAMPSIA Compared with placebo: Magnesium supplements seem no more effective at reducing the risk of pre-eclampsia ( moderate-quality evidence ).
Salt restriction
DEVELOPMENT OF PRE-ECLAMPSIA Compared with normal dietary intake: A low-salt diet seems no more effective at reducing the risk of pre-eclampsia ( moderate-quality evidence ).
When does gestational hypertension start?
In contrast, the onset of severe gestational hypertension and/or severe preeclampsia before 35 weeks' gestation is associated with significant maternal and perinatal complications. Women with diagnosed gestational hypertension-preeclampsia require close evaluation of maternal and fetal conditions for the duration of pregnancy, ...
When is expectant management possible?
Expectant management is possible in a select group of women with severe preeclampsia before 32 weeks' gestation. Steroids are effective in reducing neonatal mortality ...
Is preeclampsia a pregnancy disorder?
Gestational hypertension and preeclampsia are common disorders during pregnancy, with the majority of cases developing at or near term. The development of mild hypertension or preeclampsia at or near term is associated with minimal maternal and neonatal morbidities. In contrast, the onset of severe gestational hypertension and/or severe ...
What tests are needed for preeclampsia?
Tests that may be needed. If your doctor suspects preeclampsia, you may need certain tests, including: Blood tests. Your doctor will order liver function tests, kidney function tests and also measure your platelets — the cells that help blood clot. Urine analysis.
How to monitor a baby's growth?
Your doctor may also recommend close monitoring of your baby's growth, typically through ultrasound. The images of your baby created during the ultrasound exam allow your doctor to estimate fetal weight and the amount of fluid in the uterus (amniotic fluid). Nonstress test or biophysical profile.
How long after first blood pressure test can you get a second blood pressure test?
Having a second abnormal blood pressure reading four hours after the first may confirm your doctor's suspicion of preeclampsia. Your doctor may have you come in for additional blood pressure readings and blood and urine tests.
Can you be hospitalized for preeclampsia?
Severe preeclampsia may require that you be hospitalized . In the hospital, your doctor may perform regular nonstress tests or biophysical profiles to monitor your baby's well-being and measure the volume of amniotic fluid. A lack of amniotic fluid is a sign of poor blood supply to the baby.
What tests are done to determine if a mother has preeclampsia?
Tests for the mother might include blood and urine tests to see if the preeclampsia is progressing, such as tests to assess platelet counts, liver enzymes, kidney function, and urinary protein levels. Tests for the fetus might include ultrasound, heart rate monitoring, assessment of fetal growth, and amniotic fluid assessment.
How long after delivery can you get preeclampsia?
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends that healthcare providers closely monitor women who had high blood pressure or preeclampsia during pregnancy for 72 hours after delivery, either at home or in the hospital. 5 Because postpartum preeclampsia and eclampsia can progress quickly and can have serious effects, it is important to get treatment immediately.
How long does it take for preeclampsia to go away?
The symptoms of preeclampsia usually go away within 6 weeks of delivery. 3.
What tests are done for a fetus?
Tests for the fetus might include ultrasound, heart rate monitoring, assessment of fetal growth, and amniotic fluid assessment. Anticonvulsive medication, such as magnesium sulfate, might be used to prevent a seizure. In some cases, such as with severe preeclampsia, the woman will be admitted to the hospital so she can be monitored closely ...
What is the purpose of hospitalization for a fetus?
Hospitalization to provide intravenous medication to control blood pressure and prevent seizures or other complications as well as steroid injections to help speed up the development of the fetus's lungs 4.
What are the symptoms of postpartum preeclampsia?
The most common warning symptoms in these cases were headache, vision changes, and nausea or abdominal pain.
What is the treatment for high blood pressure?
It may also include medications to treat or prevent seizures.
How much did preeclampsia increase between 1987 and 2004?
In the United States, the rate of preeclampsia increased by 25% between 1987 and 2004 3. Moreover, in comparison with women giving birth in 1980, those giving birth in 2003 were at 6.7-fold increased risk of severe preeclampsia 4.
What is the leading cause of maternal mortality worldwide?
ABSTRACT: Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy constitute one of the leading causes of maternal and perinatal mortality worldwide. It has been estimated that preeclampsia complicates 2–8% of pregnancies globally 1. In Latin America and the Caribbean, hypertensive disorders are responsible for almost 26% of maternal deaths, ...
Why is pre-eclampsia important?
Early diagnosis of pre-eclampsia is crucial as it allows for appropriate management that will decrease the progression to pre-eclampsia with severe features and eclampsia, and as a result, reduce maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality. Thus, obstetricians should always have a high index of suspicion for the diagnosis of pre-eclampsia if a parturient at term with normal baseline blood pressures in early pregnancy presents to her prenatal care visit with new onset elevation of blood pressure at or above 140 / 90 mmHg. It is important that the history and physical exam be specific for the signs and symptoms of pre-eclampsia.
When should a woman be delivered for pre-eclampsia?
Parturients who meet diagnostic criteria for pre-eclampsia with severe features at 34 weeks or beyond should be delivered, as risks of expectant management outweigh the risks of delivery. Difficulties in management arise in women at gestations less than 34 weeks with severe features. Definitive cure for this disease requires immediate delivery, which will result in significant neonatal morbidity and mortality due to premature birth; however, prolonging the pregnancy to allow in utero fetal maturation could result in fetal demise and further jeopardize maternal health.
What is the definition of eclampsia?
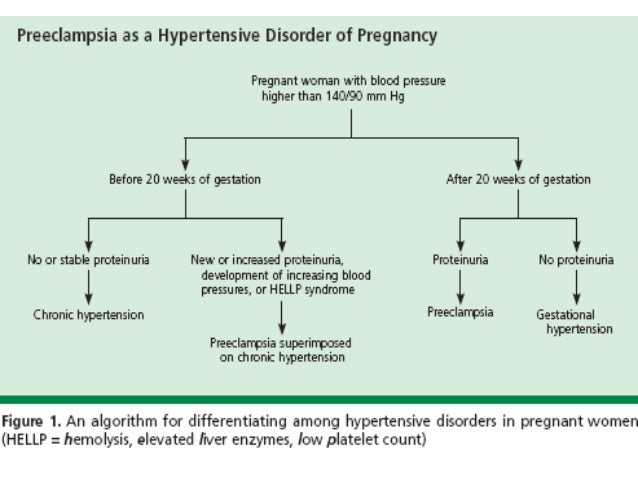
Eclampsia is defined as development of generalized tonic-clonic seizure not due to another cause in a woman with pre-eclampsia. Gestational hypertension is a diagnosis and is defined as new onset elevation of blood pressure (140/90 mmHg or greater) without proteinuria after 20 weeks gestation (previously known as pregnancy-induced hypertension).
What is pre-eclampsia?
I. What Every Physician Needs to Know. Pre-eclampsia is a syndrome of unknown etiology complicating human pregnancy. It is characterized by the new onset of hypertension and proteinuria after 20 weeks gestation and may involve multiple organ systems. While severe pre-eclampsia and eclampsia are uncommon, they can be catastrophic and are one ...
How far apart should blood pressure be measured during pregnancy?
The first diagnostic test would be blood pressure measurement. To diagnose hypertension in pregnancy, an elevated reading of 140/90 mm Hg or greater must be obtained on two separate occasions at least 4 hours apart but within a period of 7 days.
When can you take corticosteroids for pre-eclampsia?
Pre-eclampsia without severe features and mild gestational hypertension before 37 weeks is typically managed expectantly to allow in-utero fetal maturation. Corticosteroids are administered to enhance fetal lung maturity in patients who develop pre-eclampsia prior to 37 weeks. After an initial period of evaluation in the hospital, outpatient management might be considered for the stable and compliant parturient at a preterm gestation (< 37 weeks) if fetal and maternal evaluations are reassuring and consistent with either mild gestational hypertension or pre-eclampsia without severe features.
How many deaths are caused by pre-eclampsia?
While severe pre-eclampsia and eclampsia are uncommon, they can be catastrophic and are one of the leading causes of maternal death and contribute significantly to the rate of premature birth. Between 50,000 and 75,000 (14%) of worldwide maternal deaths per year are attributable to pre-eclampsia and eclampsia.
