Which hep C treatment is best?
Hepatitis C is treated using direct-acting antiviral (DAA) tablets. DAA tablets are the safest and most effective medicines for treating hepatitis C. They're highly effective at clearing the infection in more than 90% of people.
Which is better Epclusa or Mavyret?
If you have liver disease, Epclusa may be a better treatment choice for you. Severe scarring of your liver. Mavyret isn't used for treating hepatitis C if you have severe cirrhosis. However, Epclusa can be used with the drug ribavirin for this purpose.
Which hep C genotype is the easiest to treat?
Summary PointsIn the DAA era, HCV genotype 3 has emerged as the most difficult HCV genotype to treat.For treatment-naïve adults without cirrhosis, two regimens are recommended with equal evidence rating: (1) glecaprevir-pibrentasvir for 8 weeks, or (2) sofosbuvir-velpatasvir for 12 weeks.More items...•
What is the standard of treatment for hep C in the early 1990's when Janie was first diagnosed?
The early 1990s The first treatment for hepatitis C came in the 1980s, by way of a series of protein-based injections called recombinant interferon-alfa (IFNa).
What is the difference between Mavyret and Harvoni?
Mavyret is approved to treat chronic HCV genotypes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 infection in patients without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A), whereas Harvoni is only approved to treat genotypes 1, 4, 5, or 6. In addition, Mavyret is typically given for only 8 weeks, whereas Harvoni is given for 12 weeks.
Which is better Epclusa vs Harvoni?
Which is more effective: Epclusa or Harvoni? Although both Epclusa and Harvoni are effective for treating hepatitis C, Epclusa may cure a greater percentage of people than Harvoni does. Epclusa was approved in 2016 and was the first medication approved that was effective at treating all six hepatitis C genotypes.
Are all hep C genotypes curable?
Once-daily combination pills that can treat all genotypes of hepatitis C infection are curing almost everyone who completes a course of treatment, and drop-out rates during treatment are low, large 'real-world' cohort studies reported this week at The International Liver Congress in Vienna.
What genotypes does Harvoni cover?
Who can use Harvoni? Harvoni is indicated for use by adults with chronic hepatitis C, meaning infection lasting more than six months. It is approved for people with HCV genotypes 1 or 4, and for some people with genotype 3.
How long can you live with Hep C genotype 3?
Results. A total of 180 patients were enrolled. Of these, 86, 78, and 16 had genotype 1, genotype 2, and genotype 3 HCV-related HCC, respectively. The median age was 66.0 years, and the median overall survival was 28.6 months.
When did Harvoni come out?
Harvoni received regulatory approval for the treatment of chronic HCV genotype 1 infection in adults in the United States in October 2014 .
When did Hep C get cured?
I would never have imagined that during the course of my career I would witness the discovery of what came to be known as hep C and the development of a cure for nearly all patients with chronic hepatitis C in 2014.
How to treat hepatitis C side effects?
You should eat a well-balanced, nutritious diet and make sure to drink plenty of water to avoid dehydration. It’s also important to avoid smoking and alcohol since these habits can have ...
How to help HCV side effects?
They can help relieve these side effects by reducing your dosage or switching you to another medication.
How many people have hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a stubborn but common virus that attacks the liver. About 3.5 million people in the United States have chronic, or long-term, hepatitis C. It can be difficult for the human immune system to fight HCV.
Can DAAs cure HCV?
Today, DAAs are the standard of care for those with chronic hepatitis C. Unlike previous treatments, which could only help people manage their condition, DAAs can cure HCV infection at a much higher rate. These drugs may be available as individual drugs or as part of a combination therapy. All of these medications are taken orally.
Does ribavirin cause nausea?
changes in your ability to taste. memory loss. trouble concentrating. difficulty sleeping. muscle pain. hemolytic anemia. A more serious side effect of ribavirin relat es to pregnancy.
Can interferons cure HCV?
That’s largely because DAAs cause far fewer side effects than interferons do. DAAs are also able to cure HCV with higher frequency.
What is the treatment for hepatitis C?
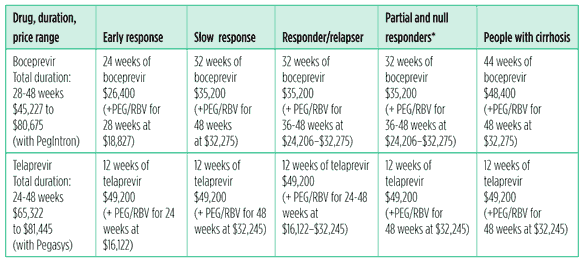
The standard treatment was typically interferon along with other drugs -- usually ribavirin and either boceprevir ( Victrelis) or telaprevir ( Incivek ). But many people have a hard time with interferon’s side effects, which include fatigue, fever, chills, and depression.
How long does it take for hepatitis C to heal?
Depending on the type of hepatitis C infection, these can often cure the disease in 8 to 12 weeks. Other treatment options include: daclatasvir ( Daklinza ); ombitasvir-paritaprevir-ritonavir ( Technivie ); or some combinations of simeprevir ( Olysio ); sofosbuvir ( Sovaldi ); peginterferon or ribavirin.
How many mg of mavyret is recommended daily?
Glecaprevir and pibrentasvir ( Mavyret) is a fixed-dosage combination pill. The recommended dosage is 3 tablets daily. This medication offers a shorter treatment cycle of 8 weeks for adult patients with HCV who don’t have cirrhosis and who have not been previously treated.
How long after stopping ribavirin can I take it?
Also, you’ll need to use two methods of birth control to prevent pregnancy in you or your partner while taking ribavirin and for 6 months after you stop. Sofosbuvir-velpatasvir-voxilaprevir ( Vosevi) You’ll take it once a day for 12 weeks. It’s OK for people who have cirrhosis and have already had some treatment.
How long does ribavirin last?
Ribavirin. This comes as a tablet, capsule, or liquid. You take it with food twice a day, in the morning and evening, for 24 to 48 weeks or longer.
What tests are done to determine the viral load of HCV?
During your treatment, you'll also get blood tests. They measure your "viral load" -- the amount of HCV that's in your body.
How long does it take to take a cirrhosis pill?
You'll take three tablets a day for 8 weeks if you don't have cirrhosis (liver scarring) and haven’t been treated before. You’ll get treatment longer if your disease is more advanced.
How long do you take ribavirin and interferon?
Another big difference between interferon/ribavirin treatment and newer DAAs: The duration. With interferon, you might have to take it for up to a year; with DAAs, you generally take them for just eight to 12 weeks. The lengthy stint on earlier types of drugs could be responsible for complications: In 2001, Karen Hoyt, 62, of Tulsa, OK, underwent HCV treatment with interferon, ribavirin, and a now-discontinued protease inhibitor. She was supposed to be on medication for 48 weeks, but at week 44, an esophageal bleed-out landed her in intensive care. “My doctor had to discontinue treatment, but thankfully I had been cured,” she says.
Does interferon kill HCV?
The likely reason interferon and ribavirin had more side effects and less effectiveness? These drugs don’t kill HCV, but instead stimulate the immune system to attack it. The constant immune response triggers flu-like symptoms throughout treatment. (“One of my patients said it was like 12 months of PMS with a cold,” says Dr. Dieterich.) DAAs, or direct-acting antivirals, attack the virus itself by targeting HCV-encoded proteins key to the virus’ replication, effectively stopping it in its tracks. Once the infection is addressed, the liver has a chance to heal and regenerate.
Is Incivek a direct acting antiviral?
In 2011, Incivek (telaprevir) and Victrelis (boceprevir) were approved as direct-acting antiviral (DAA) agents. Unfortunately, they introduced more side effects, including rashes and nausea, making HCV treatment go from bad to worse, says Douglas Dieterich, M.D., professor of medicine and director of outpatient hepatology at the Icahn School of Medicine, Mount Sinai Health System in New York. Alternative DAA medications with fewer side effects and better success rates were soon developed, and a handful were approved between 2014 and 2017. “It happened faster than anyone anticipated,” Dr. Dieterich notes.
Does Harvoni cause headaches?
In 2014, researchers conducting a study of HCV patients treated with a new drug, Harvoni (ledipasvir/sofosbuvir), found fatigue, headache, and nausea were the most common side effects: Not perfect, but way better than a rash and the flu! In addition, they found that patients had higher adverse reactions when ribavirin (the drug traditionally used in conjunction with HCV treatment) was added to their DAA treatment. Researchers looked at Harvoni alone at 8 weeks versus Harvoni combined with ribavirin. A total of 21% of patients with just Harvoni experienced fatigue; 35% with ribavirin added felt tired, indicating its adverse effects.
What is the purpose of taking hepatitis C medication?
The purpose of taking medications to treat hepatitis C is to: Clear the virus from your bloodstream. Slow the advancement of inflammation and scarring of your liver. Lower your chances of developing cirrhosis or liver cancer.
What are the factors that affect hepatitis C?
The most important factors that impact treatment results include: 1 Taking medications as prescribed and not missing doses 2 Your hepatitis C genotype 3 The presence of cirrhosis (severe scarring of the liver)
What is a non responder for hepatitis C?
Nonresponse: When the hepatitis C virus does not become undetectable as a result of treatment, you are considered a non-responder. There are two types, 1) partial response is where the viral load decreases, and 2) null-response is where the viral load never drops.
Is hepatitis C a cure?
The goal of all hepatitis C treatment is to achieve SVR. This is considered a cure. Adherence to prescribed medication regimens will increase your chances of a cure and minimize your risk for long-term complications associated with hepatitis C.
Can you breastfeed while on hepatitis C?
Other medical conditions, including liver disease not related to HCV. If you are currently breastfeeding or if you plan to breastfeed while on therapy; it is not currently known if hepatitis C medications pass into the breast milk. If you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
How many people die from hepatitis C each year?
Americans have chronic hepatitis C. About 19,000 of these people die each year from cirrhosis or liver cancer. Fortunately, recent advancements in the fight against this virus have changed the outlook for people with HCV. New drugs have transformed the disease from one that can, at best, be controlled to one that can be cured for most people who ...
What is the new drug called for HCV?
Trusted Source. of people who take them, depending on the type of HCV infection and treatment exposure. These new drugs are called direct-acting antivirals (DAAs).
What is the liver infection?
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that attacks the liver. Infection with hepatitis C can lead to serious liver disease, including cirrhosis and cancer. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is transmitted by exposure to blood or other bodily fluids that contain HCV.
What are the criteria for liver disease?
These criteria may be based on: the severity of liver disease. whether the person avoids alcohol and drug use. whether the drug’s prescribed by a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. the life expectancy of the person seeking treatment. whether less expensive treatments could be used first.
What do you do if your insurance denies you treatment for HCV?
These groups provide assistance with all aspects of HCV treatment. For instance, if your insurer denies treatment, you can appeal the decision with help from one of these groups. Your doctor can also help in this situation.
When was HCV approved?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first of these medications for HCV treatment in 2011. Several more medications have been approved since that time. Most of these individual drugs are effective for specific strains, or genotypes, of HCV.
Who pays for HCV medications?
These groups negotiate drug prices directly with the pharmaceutical manufacturers and don’t pay full price for the drugs.
How many people have hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C is a major public health challenge that affects 70 million people and is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality globally (1, 2). The availability of simple and effective oral direct acting antiviral (DAA) therapies of short duration with minimal side effects make HCV cure a possibility for those who have access to treatment. The ability to cure hepatitis C has also fueled optimism regarding the potential for HCV elimination. Indeed, the World Health Organization has set lofty HCV elimination targets of 90% diagnosed, 80% treated, and 65% reduction in mortality by 2030 (3).
What genotype is RCT of short duration pegylated interferon and ribavirin?
RCT of short duration pegylated interferon and ribavirin in genotype 2 and 3 HCV
Does HCV cure?
Effective HCV treatments lead to HCV cure in over 95% of patients treated with these oral DAA regimens (4). However, because HCV infection does not confer protective immunity, individuals who have cleared a previous infection either spontaneously or after treatment induced clearance remain at risk for reinfection. Reinfection is defined as the reoccurrence of HCV viremia after a previously cleared infection (5).
Does HIV increase the risk of reinfection?
The role of HIV infection in increasing the risk of HCV reinfection is not completely clear. HIV infection is associated with an approximately 3-fold reduction in rates of spontaneous recovery from an acute HCV infection (23, 24). As such, one may postulate that HIV-infected persons have similar rates of HCV reinfection to HIV uninfected persons but may be less likely to spontaneously clear these reinfections and are thus more likely to have reinfections detected. Alternatively, it is also possible that HIV-infected persons studied in these predominantly male cohorts may represent HIV-infected MSM with high risk sexual practices which led to both initial HCV infection and reinfection. The rates of HCV reinfection in HIV-infected MSM in the interferon era range from 5.3-13.2/100PY (10, 14, 25). These HCV reinfection data among MSM also suggest that a subgroup of these individuals will go on to have multiple HCV reinfections (10). An additional concern is the risk of transmission of HCV virus with resistant variants (26).
What happens if you have hepatitis C?
Without treatment of a chronic infection, about 75% to 85% of people who have it get a long-term infection called chronic hepatitis C. If the condition goes untreated, it can lead to: Cirrhosis, or scarring of the liver. Liver cancer.
How long can you live with hep C?
But about 70% to 80% of people with will get chronic help C. Within 20 years, about 20% to 30% of those people will get cirrhosis. From there, it depends on what type of cirrhosis you have, your treatment, and if you can get a liver transplant.
How does hep C spread?
Hepatitis C spreads through blood-to-blood contact. You could infect a loved one if you accidentally use their toothbrush or cut yourself and don’t clean up the blood properly. People who get hep C treatment greatly lower the odds that they will pass the virus to someone else.
How long does it take for hep C to clear?
New drugs can clear the virus from your body in a few months with fewer side effects than older medicines. If there’s no virus in your blood 3 months after treatment, you’re considered cured.
What to do if you aren't sure if you have hepatitis C?
If you aren’t sure if you have hepatitis C, talk to your doctor to see if you should get tested. Learn why you should get tested for hepatitis C.
How long can you go without knowing you have hepatitis C?
When you have hepatitis C, it’s possible to go for years without knowing you’re infected. If you feel fine, does that mean you don’t need to treat the infection?
Does hepatitis C cause cancer?
Cancers. People with hepatitis C are more likely to get non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. That’s a type of cancer that starts in the immune system. The virus also raises your odds of liver cancer and bile duct cancer.

Treatment
- Hepatitis C virus is treated with all-oral medications. These pills, called antiviral medications , are usually taken once per day. These antiviral medications are extremely good at attacking the virus and preventing it from multiplying. Antiviral medications were not the original treatment for hep…
Mechanism
- In an untreated state, the hepatitis C virus infects the cells of the liver and then continuously lives there, making copies of itself that circulate in the bloodstream. Antiviral medications can destroy the ability of the virus to reproduce, so the amount of virus in the bloodstream then decreases. The amount of virus in the blood is measured by a viral load (also called HCV RNA).
Prognosis
- Treatment is successful when the viral load drops to undetectable levels, which means the virus cannot be detected in the bloodstream at all. The viral load becomes undetectable during treatment and remains undetected after treatment has ended. If there is still no detectable virus in the blood 12 weeks after the end of the treatment, the treatment was successful. This is called …
Symptoms
- The medications will usually cause a very big drop in the viral load within the first two weeks. Some patients will see their viral load become undetectable very early, such as by the fourth week. For other patients, it can take longer until their viral load becomes undetectable.
Results
- Your provider will meet with you during treatment to review how well you are tolerating treatment and review laboratory results. Laboratory tests help keep tabs on your health, track the viral load, and determine your response to treatment. You will be given specific dates to go get your blood tested at the lab during and after the treatment.
Access
- For more about hepatitis C treatment, see our patient information , contact the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Hepatitis Toll-Free Information Line at 1-888-4 HEPCDC (1-888-443-7232), or visit the CDC website at http://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/index.htm .