
Medication
Introduction. Chronic stable angina has a consistent duration and severity, and is provoked by a predictable level of exertion. It can also be provoked by emotional stress. The pain is relieved by rest or short-acting nitrates. 2 The aim of medical therapy is to minimise symptoms and retard disease progression.
Procedures
Stable angina pectoris is characterised by typical exertional chest pain that is relieved by rest or nitrates. Risk stratification of patients is important to define prognosis, to guide medical management and to select patients suitable for revascularisation. Medical treatment aims to relieve angina and prevent cardiovascular events.
Self-care
The presence of chronic angina approximately doubles the risk of major cardiovascular events (CVEs). 1 Chest pain that can be characterized as chronic stable angina typically is produced with physical exertion and is relieved by rest and/or nitroglycerin.
Nutrition
If your angina is unstable, seek urgent medical care. Other types of angina include variant or Prinzmetal's angina — a rare type caused by a spasm in the coronary arteries — and microvascular angina, which can be a symptom of disease in the small coronary artery blood vessels.
What is the treatment for chronic stable angina?
What is stable angina pectoris?
What is chronic stable angina (Cha)?
When should I seek urgent medical care for angina pectoris?
How is chronic stable angina treated?
How is stable angina treated?Lifestyle. Certain lifestyle adjustments can help prevent future episodes of stable angina. ... Medication. A medication called nitroglycerin effectively relieves pain associated with stable angina. ... Surgery. A minimally invasive procedure called angioplasty is often used to treat stable angina.
What is the standard treatment for angina pectoris?
Nitrates are often used to treat angina. Nitrates relax and widen the blood vessels so more blood flows to the heart. The most common form of nitrate used to treat angina is nitroglycerin. The nitroglycerin pill is placed under the tongue.
What is the first-line treatment for stable angina?
Beta-blockers lessen anginal symptoms by reducing heart rate and myocardial contractility and decreasing blood pressure. This results in decreased myocardial oxygen demand. They can be considered as the first-line treatment for reducing the symptoms of stable angina.
Which medication combination therapy is recommended for chronic stable angina?
Monotherapy with a beta blocker or a nitrate is the first choice for patients with stable angina if there are no contraindications. If monotherapy fails to produce improvement, the combination of a beta blocker and a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker or a nitrate may relieve symptoms and mitigate ischemia.
Which of the following is recommended first-line for risk factor modification in chronic stable angina?
Beta blockers are first-line therapy to reduce angina and improve exercise tolerance by limiting the heart rate response to exercise.
Which medications are used to prevent severe complications and even death in patients with stable angina?
β-adrenergic receptor blockers (beta-blockers) and calcium-channel blockers are considered to be first-line anti-anginal drugs and have been shown in many studies to prevent angina and myocardial ischaemia.
Is GTN used for stable angina?
Sublingual glyceryl trinitrate tablets or nitroglycerin spray remain the treatment of choice for rapid relief of acute symptoms and anticipated angina.
Which classes of drugs are used in the treatment of angina pectoris select all that apply?
Three major classes of anti‐ischaemia drugs are currently used in the medical management of angina pectoris: β‐blockers, nitrates (short‐ and long‐acting), and calcium channel antagonists (table 1).
Why Are There Different Treatments For Each Type of Angina?
Angina is pain, discomfort or pressure in the chest, and doctors usually describe it as chronic stable angina or unstable angina. 1. Chronic stable...
What Are The Treatment Options For Chronic Stable Angina?
During an angioplasty (AN-jee-o-plas-tee), your doctor inserts a tiny balloon in your narrowed artery through a catheter that's placed in an artery...
So Which Angina Treatment Is Better — Angioplasty and Stenting Or medications?
Your medical condition will determine whether having angioplasty and stenting or taking medications will work better for you. Talk to your doctor a...
What If Your Angina Treatment Doesn't Work?
If you try medication and lifestyle changes first, but they don't relieve your angina, angioplasty and stenting may be another option. In some case...
What is the best medication for angina?
Aspirin and other anti-platelet medications reduce the ability of your blood to clot, making it easier for blood to flow through narrowed heart arteries. Nitrates. Often used to treat angina, nitrates relax and widen your blood vessels, allowing more blood to flow to your heart muscle.
How to control angina?
If your angina is stable, you might be able to control it with lifestyle changes and medicines. Unstable angina requires immediate treatment in a hospital, which could involve medicines and surgical procedures.
How to treat angina with nitrates?
Several medications can improve angina symptoms, including: 1 Aspirin. Aspirin and other anti-platelet medications reduce the ability of your blood to clot, making it easier for blood to flow through narrowed heart arteries. 2 Nitrates. Often used to treat angina, nitrates relax and widen your blood vessels, allowing more blood to flow to your heart muscle. Nitrates in pills or sprays act quickly to relieve pain during an event. There are also long-acting nitrate pills and skin patches. 3 Beta blockers. These block the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline. They help your heart beat more slowly and with less force, decreasing the effort your heart makes and easing the angina pain. 4 Statins. Statins lower blood cholesterol by blocking a substance your body needs to make cholesterol. They might also help your body reabsorb cholesterol that has accumulated in the buildup of fats (plaques) in your artery walls, helping prevent further blockage in your blood vessels. 5 Calcium channel blockers. Also called calcium antagonists, these drugs relax and widen blood vessels by affecting the muscle cells in the arterial walls. This increases blood flow in your heart, reducing or preventing angina. 6 Ranolazine (Ranexa). This anti-angina medication might be prescribed with other angina medications, such as beta blockers. It can also be used as a substitute if your symptoms don't improve with the other medications.
What to do if your angina is not working?
For most people, first steps include medications and lifestyle changes. If those don't work for you, angioplasty and stenting can be another option. Talk to your doctor if you think your treatment isn't controlling your angina well enough. May 21, 2021. Show references.
How do statins help with angina?
They help your heart beat more slowly and with less force, decreasing the effort your heart makes and easing the angina pain. Statins. Statins lower blood cholesterol by blocking a substance your body needs to make cholesterol.
What to eat when you have angina?
Include a variety of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and low-fat dairy products in your diet. Lack of physical activity. Talk to your doctor about starting a safe exercise plan. If your angina is brought on by exertion, pace yourself and take rest breaks.
What is the most common type of angina?
Types of angina. Angina is pain, discomfort or pressure in the chest. The most common types are chronic stable angina and unstable angina. Chronic stable angina. Chest pain occurs when your heart is working hard enough to need more oxygen, such as during exercise. The pain can go away when you rest.
What is the best treatment for angina?
There are many options for angina treatment, including lifestyle changes, medications, angioplasty and stenting, or coronary bypass surgery. The goals of treatment are to reduce the frequency and severity of your symptoms and to lower your risk of a heart attack and death.
How to prevent angina?
Because heart disease is often the cause of angina, you can reduce or prevent angina by working on reducing your heart disease risk factors. Making lifestyle changes is the most important step you can take.
What is ECP in angina?
It's a treatment option for both unstable angina as well as stable angina that has not responded to other treatments. External counterpulsation (ECP). With ECP, blood pressure-type cuffs are placed around the calves, thighs and pelvis to increase blood flow to the heart. ECP requires multiple treatment sessions.
What are the best drugs to lower blood pressure?
Beta blockers also help blood vessels relax and open up to improve blood flow, thus reducing or preventing angina. Statins. Statins are drugs used to lower blood cholesterol.
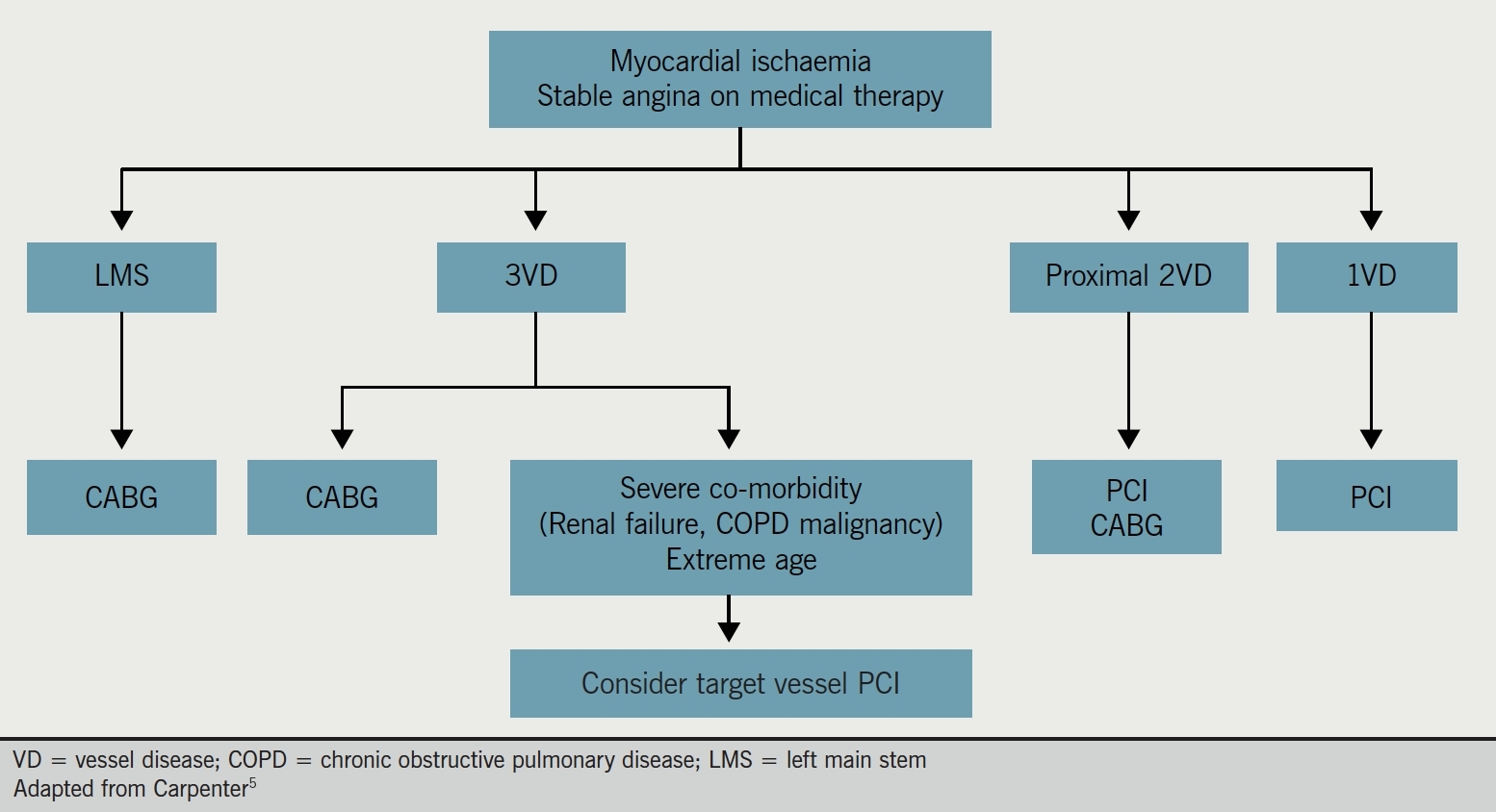
What is the procedure to bypass a narrowed heart artery?
Coronary artery bypass surgery. During coronary artery bypass surgery, a vein or artery from somewhere else in your body is used to bypass a blocked or narrowed heart artery. Bypass surgery increases blood flow to your heart and reduces or eliminates angina.
How to reduce angina risk?
Treat diseases or conditions that can increase your risk of angina, such as diabetes, high blood pressure and high blood cholesterol. Avoid large meals that make you feel overly full. Avoiding stress is easier said than done, but try to find ways to relax. Talk with your doctor about stress-reduction techniques.
How does statin affect the heart?
Calcium channel blockers, also called calcium antagonists, relax and widen blood vessels by affecting the muscle cells in the arterial walls. This increases blood flow in your heart, reducing or preventing angina.
What is stable angina pectoris?
Stable angina pectoris (SAP) is the most common manifestation of myocardial ischemia. Myocardial ischemia occurs when the oxygen demand of the heart exceeds the supply. There are three factors that determine myocardial oxygen demand—heart rate, contractility, and intra-myocardial wall tension, with the latter considered the most important.
What are the goals of angina treatment?
The goals of treatment are to reduce or eliminate symptoms and prevent long-term complications, such as MI, left ventricular failure, and life-threatening arrhythmias. Lifestyle modifications, medications, and myocardial revascularization are all employed in the treatment of angina. 2
Why does angina cause calcium overload?
A greater influx of sodium results in intracellular calcium overload because of an increased influx of calcium through the sodium-calcium exchange. Angina is often associated with increases in intracellular sodium, thus resulting in increases in intracellular calcium.
How long does angina pain last?
The pain can last anywhere from 30 seconds to 30 minutes and is usually relieved with sublingual nitroglycerin (SLNTG). Any change in the quality, frequency, or duration of the pain or the precipitating factors suggests unstable angina, which requires immediate medical attention. 1.
What is mixed angina?
Some patients may have both characteristics, and this is termed mixed angina. 2. A single-cell endothelial layer separates the vascular smooth muscle from the blood. When intact, this vascular endothelium permits vasodilation and prevents thrombus and sclerotic plaque formation.
Can angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors improve endothelial function?
Endothelial function can be improved with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs), statins, and exercise. 1 The Canadian Cardiovascular Society developed a system of grading angina that is generally well accepted ( TABLE 1 ). 3.
What is the goal of treatment for angina pectoris?
The main goals of treatment in angina pectoris are to relieve the symptoms, slow the progression of disease, and reduce the possibility of future events, especially MI and premature death.
What is the effect of exercise training on ischemia?
Exercise training results in improvement of symptoms, an increase in the threshold of ischemia, and improvement of patients' sense of well-being. However, before enrolling a patient in an exercise-training program, perform an exercise tolerance test to establish the safety of such a program.
What is the primary end point of a stent?
The primary end point was death from any cause. The secondary end points were stent thrombosis, the composite end point of death or myocardial infarction, and the composite of death, MI, or a revascularization.
Does hormone replacement therapy help with cardiovascular disease?
Although early observational studies suggested a cardiovascular protective effect with the use of hormone replacement therapy, recent large randomized trials failed to demonstrate any benefit with hormone replacement therapy in the primary or secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease .
Can calcium channel blockers be used for angina?
Long-acting heart rate–slowing calcium channel blockers can be used to control anginal symptoms in patients with a contraindication to beta-blockers and in those in whom symptomatic relief of angina cannot be achieved with the use of beta-blockers, nitrates, or both.
What is the purpose of pharmacologic treatment?
Use of pharmacologic treatments to improve quality of life and/or survival, with particular attention to side effects and drug interactions. 5. Use of cardiac revascularization, when appropriate, to optimize overall health status and improve survival.
What is the pain in the chest caused by cardiac ischemia?
Women and the elderly, in particular, may present with atypical symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, mid-epigastric discomfort, or sharp (atypical) chest pain. Anginal pain caused by cardiac ischemia typically lasts minutes. The location is usually substernal, and pain can radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or arms.
What is the effect of calcium channel blockers on myocardial function?
Dihydropyridine (e.g., nifedipine, amlodipine) and nondihydropyridine (e.g., verapamil, diltiazem) calcium channel blockers produce coronary vasodilation, a reduction in myocardial contractility, and a decrease in myocardial oxygen demand.
What is the most common heart disease?
ABSTRACT: Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most common type of heart disease and the leading cause of death worldwide. Angina pectoris, a clinical syndrome characterized by discomfort typically located in the chest, neck, or left arm, is one of several clinical manifestations of CAD. The gold standard for diagnosing ...
What is the purpose of patient education?
Patient education on the causes, clinical presentation, treatment options, and prognosis of the disease, in order to encourage active participation in treatment decisions. 2. Identification and treatment of conditions that can contribute to or worsen the disease. 3.
Can beta blockers be used for angina?
However, beta-blockers should be used as first-line therapy with the goals of reducing the frequency and severity of angina and improving exercise capacity and quality of life. 6.
Does angina cause cardiovascular events?
The presence of chronic angina approximately doubles the risk of major cardiovascular events (CVEs). 1. Chest pain that can be characterized as chronic stable angina typically is produced with physical exertion and is relieved by rest and/or nitroglycerin.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment